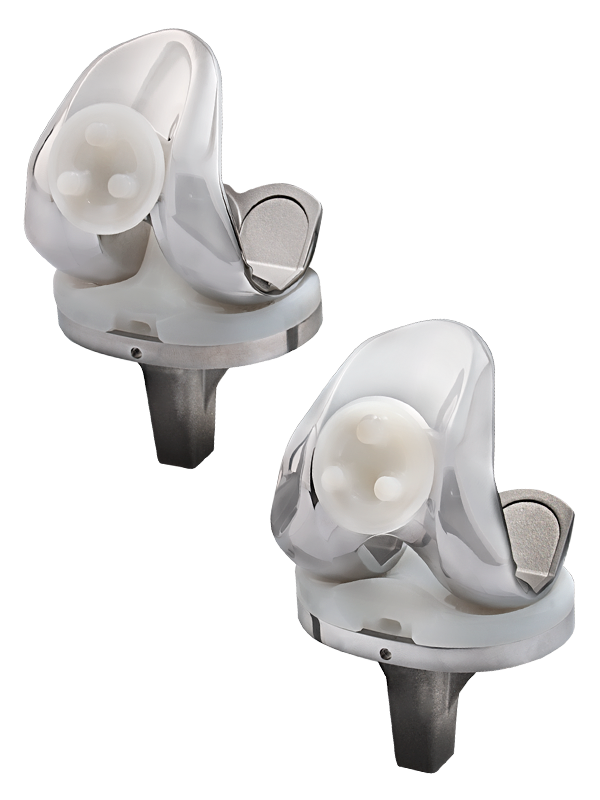
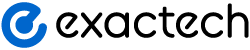The surfaces where these three bones touch are covered with cartilage, a smooth substance that cushions the bones and allows them to move easily. Healthy cartilage lets you move your knee without pain when you walk, run or go up stairs.
All remaining surfaces of the knee are covered by a thin, smooth liner that releases a special fluid to lubricate the knee. This eliminates friction, or rubbing, almost completely in a healthy knee.
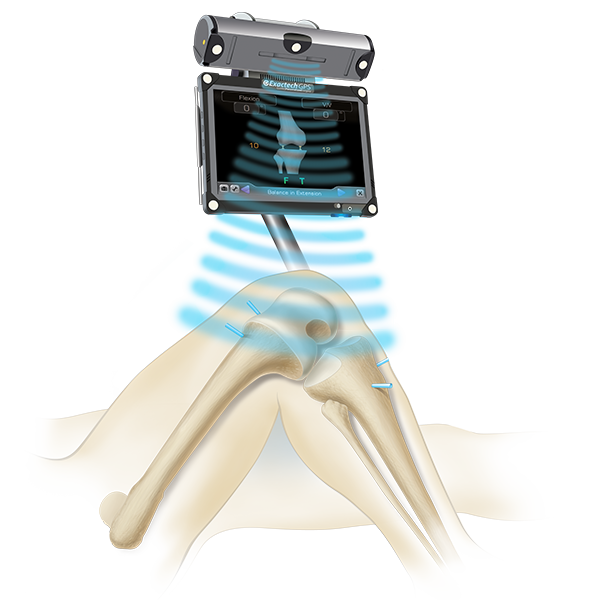
Normally, all of these components work in harmony. But disease or injury can disrupt this harmony, resulting in pain, muscle weakness and increased friction.
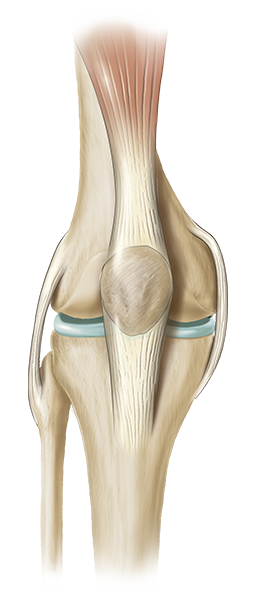
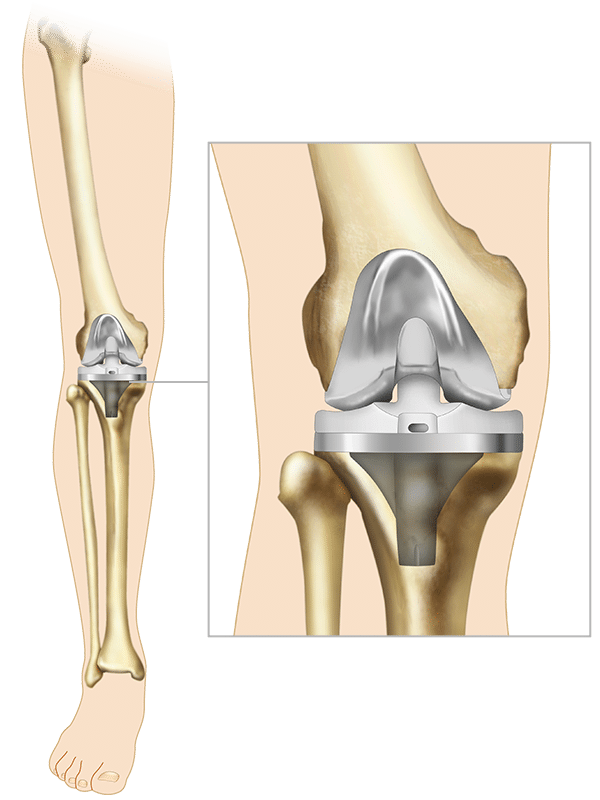
Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is a condition that causes wear and tear to your joint cartilage. It develops after years of constant motion and pressure in the joints. As the cartilage continues to wear away, the joint becomes painful and difficult to move. If non-surgical treatment options, such as medication, physical therapy or lifestyle changes like losing weight, fail to provide relief, your surgeon may recommend total knee replacement surgery.